Synergizing Melanoma Treatment: Biomarker Insights from Ariana Pharmaceuticals and Harvard
Overview
The collaborative study between Ariana Pharmaceuticals and Harvard Medical School’s Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center focuses on identifying biomarkers of synergistic drug combinations for melanoma treatment. Utilizing large-scale drug combination screening integrated with multiomics data analysis, the project aims to uncover effective therapeutic combinations that can prevent disease progression in melanoma patients derived cell lines resistant to standard treatments.
Impact
This research significantly impacts melanoma therapy by deepening the understanding of drug synergy and its underlying molecular mechanisms. By integrating extensive omics data and applying eXp.AI data analysis techniques, the study provides a methodical approach to predicting drug combinations that may yield higher therapeutic efficacy while decreasing drug doses. This approach helps optimize drug combinations in preclinical and clinical settings, paving the way for their validation in pivotal clinical trials.
Objectives
• To systematically identify biomarkers associated with synergistic effects in drug combinations using a dataset of melanoma cell lines deeply characterized at the molecular level.
• To develop a predictive model using the KEM® Platform that can efficiently suggest potential synergistic drug pairs for further testing in clinical trials
• To enhance the understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying drug synergy in melanoma, potentially leading to innovative treatment approaches.


Method
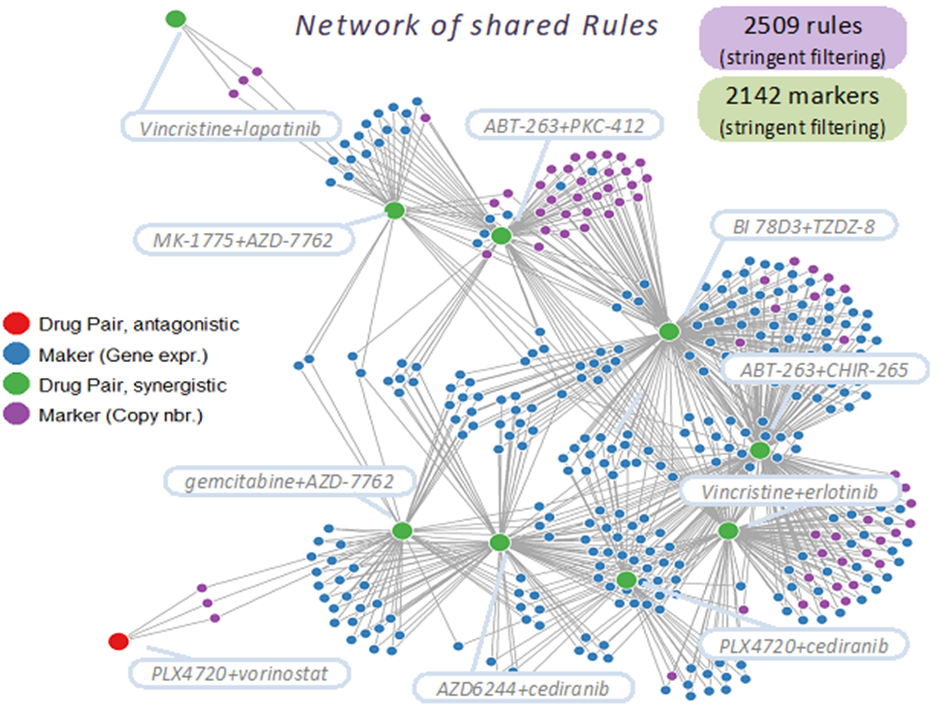
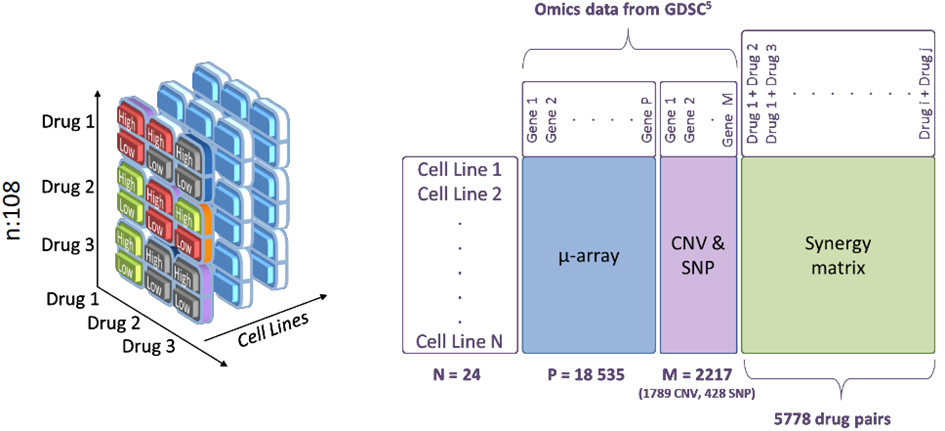
The experimental workflow involved testing 24 melanoma cell lines with 108 drugs, resulting in 5,778 drug pair combinations at multiple concentrations. The synergy of each drug pair was assessed using the Bliss independence model. Using Ariana’s KEM® eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (eXp.AI) Platform, systematic and explainable cell lines’ omics data analysis led to identification of potential biomarkers predictive of synergistic effects across cell lines and drug pairs.
Results
The study’s results highlight the effectiveness of using integrated omics data to predict drug synergy. Key findings include the identification of numerous drug pairs that exhibit potential synergistic interactions, supported by omics-derived biomarkers. These findings contribute to a more targeted approach in melanoma therapy, offering prospects for personalized treatment strategies based on specific biomarker profiles.
