Gastric Cancer: Artificial Intelligence helps identify novel single biomarkers to guide targeted precision medicine
Gastric Cancer: Ariana and academic collaborators from the Gastro Glyco Explorer consortium identify a novel single marker for Microsatellite instability (MSI), a distinct molecular subtype of gastric cancer.
Gastric cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. Adapting the therapeutic choice to the molecular diversity of the disease is a key driver for providing patients with the right targeted therapy. The Academic collaborators from the Gastro Glyco Explorer consortium aim at finding novel markers for gastric cancer using data obtained from multiple platforms including the characterization of glycans.
Tumor and serum samples were gathered from 107 patients and data was generated from 9 different experimental platforms. Analyzing this complex and heterogeneous database and generating hypotheses were possible using the KEM® Artificial Intelligence technology.
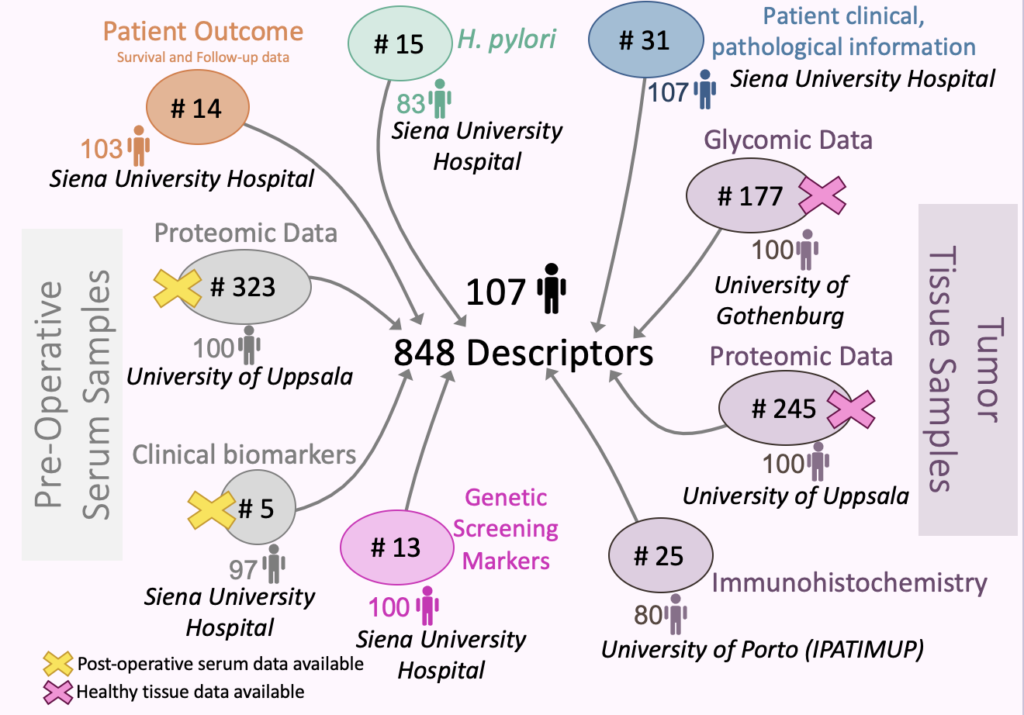

Using this integrated database, KEM® generated over 450K association rules. Exploration and visualisation of subsets of strongest rules were conducted with KEM® Query using metric filtering (Top relationships with highest association rule metrics) and semantic filtering (Top relationships with clinical and pathological relevance).
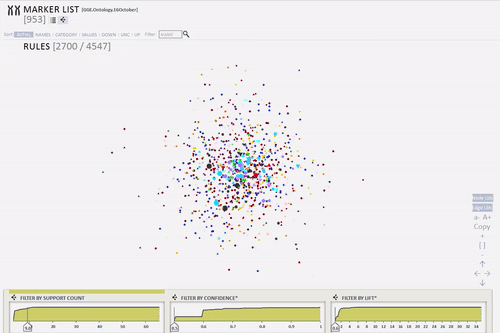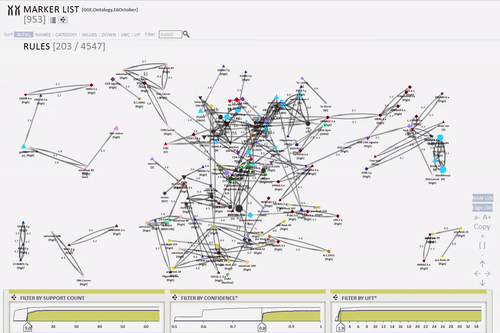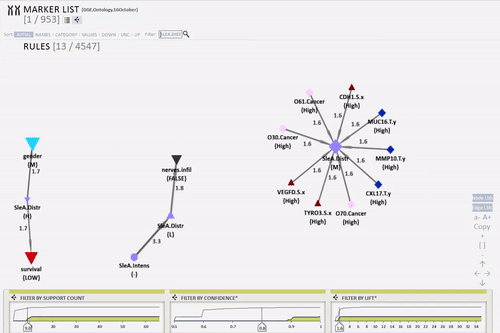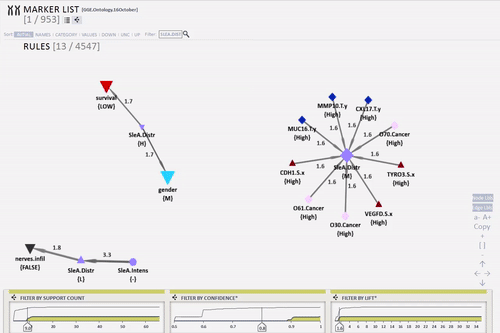

KEM® Query interactive tool helps view complex univariate association rule networks. Through a few clicks relationships of a specific descriptor in the serum or tissue alongside its clinical characteristics can be viewed.
The integrated database and KEM® results were presented at the RECOMB-Computational Cancer Biology (CCB) conference in April 2018.
Results: Recent Publication on Novel Markers
In the recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine (2018, 7(9), 256), Ariana and academic collaborators from the Gastro Glyco Explorer consortium identify a novel single marker for Microsatellite instability (MSI), a distinct molecular subtype of gastric cancer linked with PD-L1 expression.
The identified biomarker (94% specificity, 69% sensitivity, 80% NPV, 90%PPV) is a glycan antigen that may enable the identification of patients who could benefit from targeted therapy using the PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway.
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a distinct molecular subtype of gastric cancer. In recent years, the clinical consequences of MSI and the therapeutic opportunities to target this peculiar cancer subtype became evident. Additionally, it has been found that MSI is linked with PD-L1 expression and several specific drugs are currently used for clinical management of gastric cancer targeting the PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway.
Excelling with a specificity of 94% (16/17), sensitivity of 69.2% (9/13), negative predictive value of 80% (16/20), and positive predictive value of 90% (9/10) the TF antigen holds promise to be the long sought-after single biomarker for MSI status in gastric cancer.
The TF antigen is a simple glycan antigen that is aberrantly expressed in cancer cells due to alterations in the O-glycan biosynthesis pathway.
In summary, this published work presented for the first time strong evidence that TF is a novel, single marker of MSI in gastric cancer.
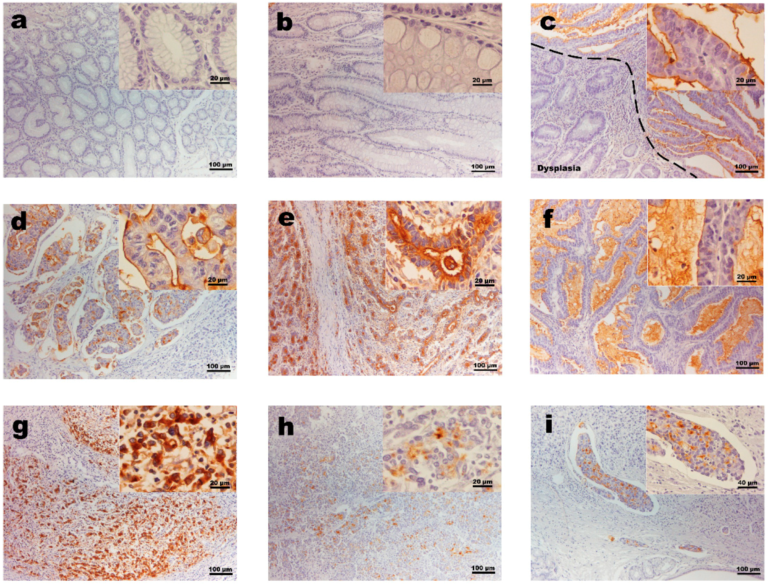

This finding lays the basis for a new line of research and shows great promise to significantly improve the identification of this distinct cancer subtype in the clinical setting.
