Real World Evidence: eXp AI-driven Disovery of Genomic Biomarkers for Liver Toxicity Risk: A UK Biobank Case Study
Overview
This study by Ariana Pharmaceuticals harnessing the UK Biobank, explores the use of explainable Artificial Intelligence (eXp AI) to identify genomic biomarkers linked to increased mortality risk in toxic liver disease. Leveraging the proprietary KEM® (Knowledge Extraction and Management) platform, genomic and clinical data from 225 patients diagnosed with toxic liver disease within the UK Biobank cohort were analyzed.
By achieving 85% accuracy in predicting mortality using the KEM®-selected SNPs- compared to 68.9% for standard Machine Learning models without genomic pre-selection- the research underscores the transformative potential of AI-driven biomarker discovery for safer, more personalized medicine.
Impact
-
- The findings represent a major advance in pharmacogenomic safety biomarker discovery- a field with few validated markers compared to efficacy biomarkers. The study demonstrates how explainable AI can uncover rare but clinically meaningful variants, providing interpretable insights to guide risk stratification and patient selection in therapies with potential hepatotoxicity (e.g., PI3K inhibitors).
By achieving 85% accuracy in predicting mortality using the KEM®-selected SNPs- compared to 68.9% for standard Machine Learning models without genomic pre-selection- the research underscores the transformative potential of AI-driven biomarker discovery for safer, more personalized medicine.
These results pave the way for the integration of genomic safety biomarkers into regulatory and clinical workflows, potentially reducing adverse outcomes and drug withdrawals related to liver toxicity.
Objective
The primary objective of the study was to identify genomic biomarkers associated with increased mortality in toxic liver disease, which could serve as predictive indicators of liver toxicity risk in drug-exposed populations. Secondary objectives included:-
- ● Evaluating the clinical and genomic factors linked to survival outcomes in patients with toxic liver disease (ICD-10 K71).
- ● Assessing the predictive performance of AI-driven biomarker selection compared to traditional statistical and random models.
- ● Demonstrating the interpretability and clinical utility of explainable AI methods for pharmacogenomic applications.
Method
Ariana Pharma’s experts used the UK Biobank dataset, encompassing over 500,000 participants with comprehensive clinical and genomic information. From this, 225 individuals diagnosed with toxic liver disease were selected (excluding non-medical causes of death).Key Steps
-
-
- 1. Data Integration:
- ● KEGG Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) pathway.
- ● Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) models for liver injury.
- 2. AI-Based Analysis (KEM®): The KEM® explainable AI platform applied Formal Concept Analysis and Association Rule Mining to identify statistically and biologically relevant associations between variables and mortality. This method captures both strong and weak multivariate interactions, even among rare variants.
- 3. The selected SNPs were evaluated using LASSO regression models with 10-fold nested cross-validation (20 replicates) to compare predictive accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity against models built on random SNP subsets.
-

Result
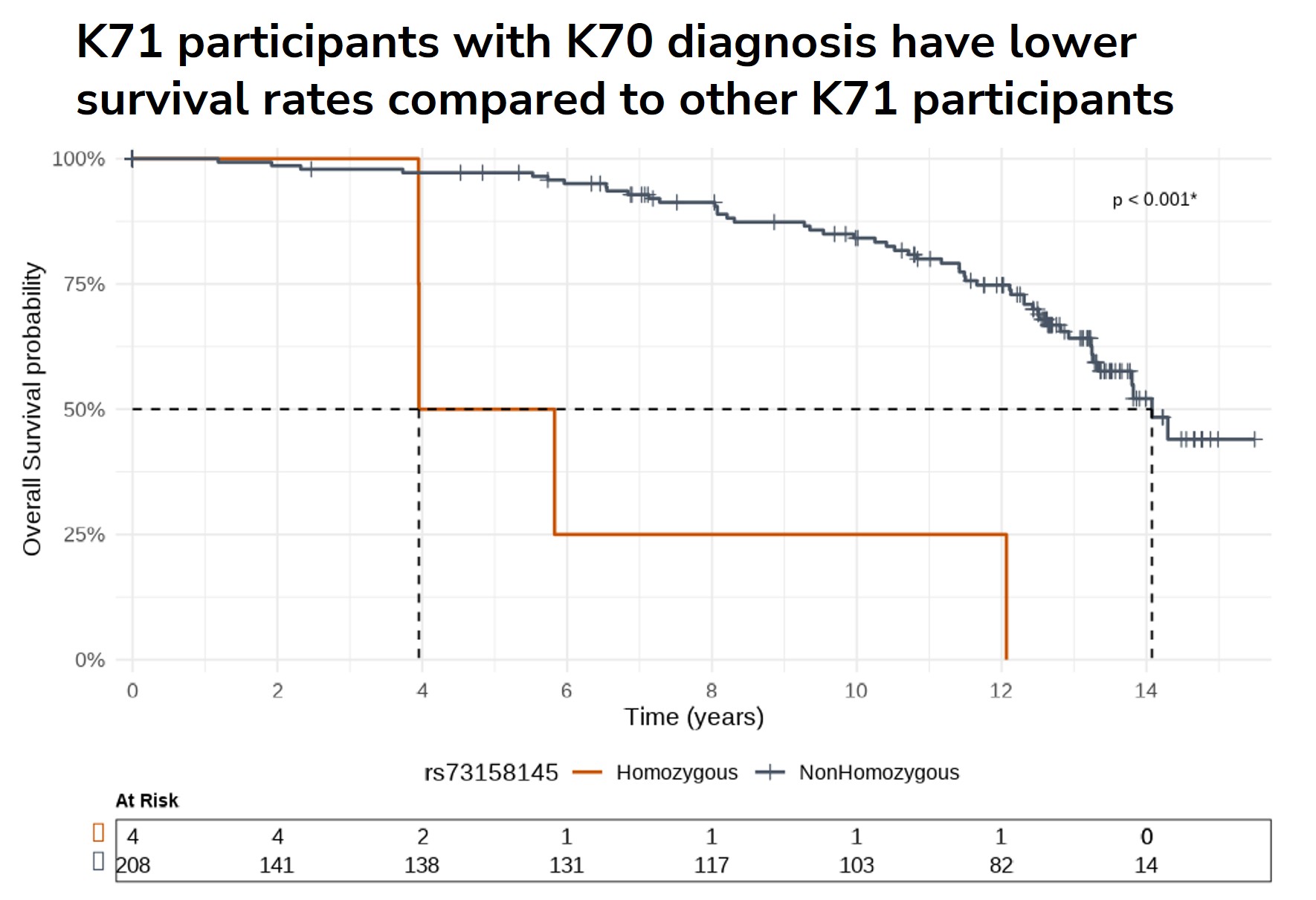
The KEM® platform identified 15 SNPs significantly correlated with increased mortality risk in toxic liver disease:- ● 1 SNP (rs73158145 in PRKAG2) from the KEGG NAFLD pathway.
- ● 14 SNPs from AOP pathway genes, including regulatory and missense variants..
Highlights
- ● The PRKAG2 rs73158145 variant reduced median survival by 3.5-fold among homozygous carriers.
- ● The AI-selected SNP model achieved 85% mean accuracy, 66.2% sensitivity, and 91.8% specificity, outperforming random SNP models (mean sensitivity 9.6%).
- ● Identified variants exhibited hazard ratios ranging from 2.55 to 8.91, indicating strong prognostic value.
- These findings validate the clinical potential of AI-driven, explainable biomarker discovery for predicting severe outcomes like drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and support future validation in independent cohorts (e.g., FinnGen).
Summary
This case study illustrates how Ariana Pharmaceuticals’ KEM® explainable(eXp) AI platform can reveal interpretable genomic signatures of safety risk, bridging a critical gap in personalized pharmacovigilance. The approach reduces vast genomic search spaces into actionable insights, setting the stage for eXp.AI-enabled clinical safety biomarker qualification and precision drug development.